|
使用多个NRF24L01模块的Arduino无线网络 在理解了上个示例之后,我们可以继续学习本篇文章的主要示例,然后搭建一个由5个Arduino开发板相互通信的无线网络。 以下是该示例的框图。
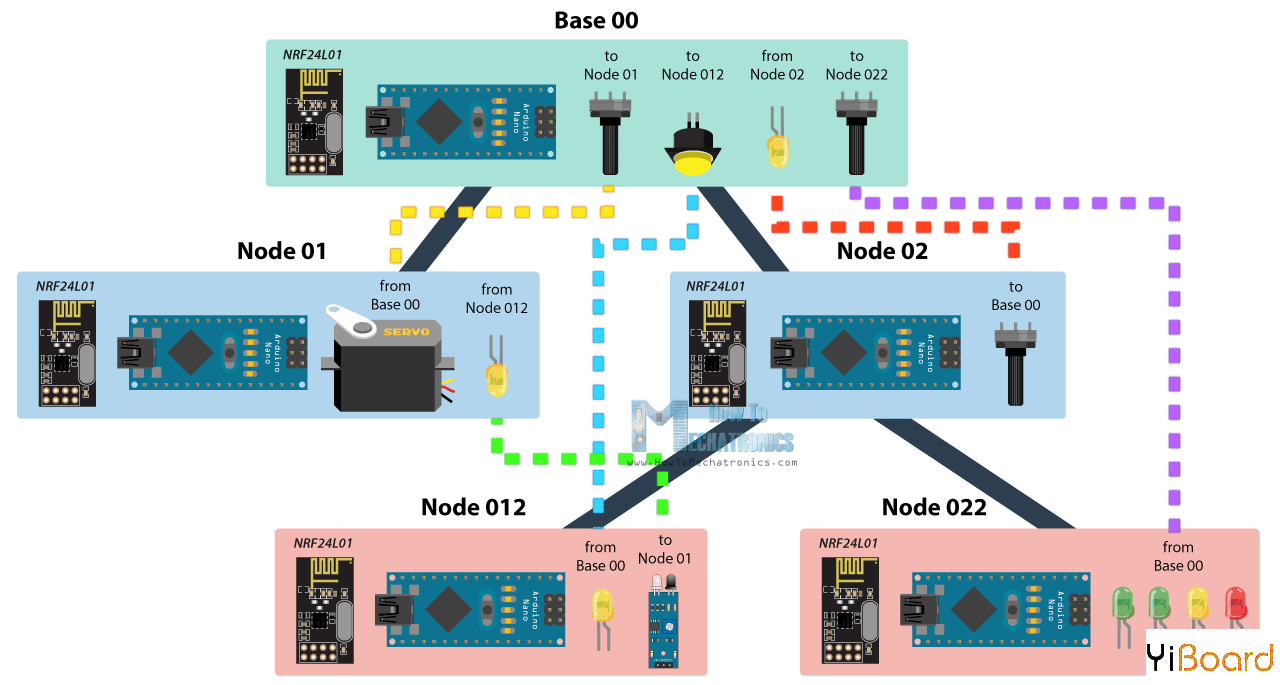
因此,从基本节点开始,我们将使用电位器控制节点01处的伺服电机,使用第二个电位器,我们将控制节点022处的LED,使用按钮我们将控制节点012处的LED,基本节点的LED将使用节点02处的电位器进行控制。同样使用节点012处的红外传感器,我们将控制节点01处的LED。因此我们可以注意到该示例解释了如何同时发送和接收数据, 以及如何与来自不同分支的节点通信。 我们现在来看看Arduino代码。
基本节点00的代码 - /*
- Arduino Wireless Network - Multiple NRF24L01 Tutorial
- == Base/ Master Node 00==
- by Dejan, www.HowToMechatronics.com
- Libraries:
- nRF24/RF24, https://github.com/nRF24/RF24
- nRF24/RF24Network, https://github.com/nRF24/RF24Network
- */
- #include <RF24Network.h>
- #include <RF24.h>
- #include <SPI.h>
- #define button 2
- #define led 3
- RF24 radio(10, 9); // nRF24L01 (CE,CSN)
- RF24Network network(radio); // Include the radio in the network
- const uint16_t this_node = 00; // Address of this node in Octal format ( 04,031, etc)
- const uint16_t node01 = 01; // Address of the other node in Octal format
- const uint16_t node012 = 012;
- const uint16_t node022 = 022;
- void setup() {
- SPI.begin();
- radio.begin();
- network.begin(90, this_node); //(channel, node address)
- radio.setDataRate(RF24_2MBPS);
- pinMode(button, INPUT_PULLUP);
- pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
- }
- void loop() {
- network.update();
- //===== Receiving =====//
- while ( network.available() ) { // Is there any incoming data?
- RF24NetworkHeader header;
- unsigned long incomingData;
- network.read(header, &incomingData, sizeof(incomingData)); // Read the incoming data
- analogWrite(led, incomingData); // PWM output to LED 01 (dimming)
- }
- //===== Sending =====//
- // Servo control at Node 01
- unsigned long potValue = analogRead(A0);
- unsigned long angleValue = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // Suitable for servo control
- RF24NetworkHeader header2(node01); // (Address where the data is going)
- bool ok = network.write(header2, &angleValue, sizeof(angleValue)); // Send the data
- // LED Control at Node 012
- unsigned long buttonState = digitalRead(button);
- RF24NetworkHeader header4(node012); // (Address where the data is going)
- bool ok3 = network.write(header4, &buttonState, sizeof(buttonState)); // Send the data
- // LEDs control at Node 022
- unsigned long pot2Value = analogRead(A1);
- RF24NetworkHeader header3(node022); // (Address where the data is going)
- bool ok2 = network.write(header3, &pot2Value, sizeof(pot2Value)); // Send the data
- }
因此,在基本节点或主节点,我们需要如前所述定义库和对象,并定义主节点将向其发送数据的所有其他节点。 在loop()函数部分,我们首先不断检查是否有数据传入。 如果有,我们读取数据,将其存储到incomingData变量中,然后使用它来控制LED亮度。 这些数据实际上来自节点02的电位器。如果我们看看它的代码,我们可以注意到设置几乎是一样的。 重要的是将正确的地址分配给我们想要发送数据的位置。 本例中是主地址00。所以在读取电位器值并将其转换为0到255的合适PWM值后,我们将这些数据发送给主机。 我们在这里可以注意到我使用millis()函数以10毫秒的间隔发送数据。
节点02的代码 - /*
- Arduino Wireless Network - Multiple NRF24L01 Tutorial
- == Node 02 (Child of Master node 00) ==
- */
- #include <RF24Network.h>
- #include <RF24.h>
- #include <SPI.h>
- RF24 radio(10, 9); // nRF24L01 (CE,CSN)
- RF24Network network(radio); // Include the radio in the network
- const uint16_t this_node = 02; // Address of our node in Octal format ( 04,031, etc)
- const uint16_t master00 = 00; // Address of the other node in Octal format
- const unsigned long interval = 10; //ms // How often to send data to the other unit
- unsigned long last_sent; // When did we last send?
- void setup() {
- SPI.begin();
- radio.begin();
- network.begin(90, this_node); //(channel, node address)
- radio.setDataRate(RF24_2MBPS);
- }
- void loop() {
- network.update();
- //===== Sending =====//
- unsigned long now = millis();
- if (now - last_sent >= interval) { // If it's time to send a data, send it!
- last_sent = now;
- unsigned long potValue = analogRead(A0);
- unsigned long ledBrightness = map(potValue, 0, 1023, 0, 255);
- RF24NetworkHeader header(master00); // (Address where the data is going)
- bool ok = network.write(header, &ledBrightness, sizeof(ledBrightness)); // Send the data
- }
- }
接下来,我们从主机发送电位器数据到节点01,以控制伺服电机。
节点01的代码 - /*
- Arduino Wireless Network - Multiple NRF24L01 Tutorial
- == Node 02 (Child of Master node 00) ==
- */
- #include <RF24Network.h>
- #include <RF24.h>
- #include <SPI.h>
- #include <Servo.h>
- #define led 2
- RF24 radio(10, 9); // nRF24L01 (CE,CSN)
- RF24Network network(radio); // Include the radio in the network
- const uint16_t this_node = 01; // Address of our node in Octal format ( 04,031, etc)
- const uint16_t master00 = 00; // Address of the other node in Octal format
- Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
- void setup() {
- SPI.begin();
- radio.begin();
- network.begin(90, this_node); //(channel, node address)
- radio.setDataRate(RF24_2MBPS);
- myservo.attach(3); // (servo pin)
- pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
- }
- void loop() {
- network.update();
- //===== Receiving =====//
- while ( network.available() ) { // Is there any incoming data?
- RF24NetworkHeader header;
- unsigned long incomingData;
- network.read(header, &incomingData, sizeof(incomingData)); // Read the incoming data
- if (header.from_node == 0) { // If data comes from Node 02
- myservo.write(incomingData); // tell servo to go to a particular angle
- }
- if (header.from_node == 10) { // If data comes from Node 012
- digitalWrite(led, !incomingData); // Turn on or off the LED 02
- }
- }
- }
节点01实际上是从两个不同的节点接收数据,一个用于伺服控制,另一个用于来自节点012的红外传感器的LED控制。
节点012的代码 - /*
- Arduino Wireless Network - Multiple NRF24L01 Tutorial
- == Node 012 (child of Node 02)==
- */
- #include <RF24Network.h>
- #include <RF24.h>
- #include <SPI.h>
- #define led 2
- #define IR 3
- RF24 radio(10, 9); // nRF24L01 (CE,CSN)
- RF24Network network(radio); // Include the radio in the network
- const uint16_t this_node = 012; // Address of our node in Octal format ( 04,031, etc)
- const uint16_t node01 = 01; // Address of the other node in Octal format
- void setup() {
- SPI.begin();
- radio.begin();
- network.begin(90, this_node); //(channel, node address)
- radio.setDataRate(RF24_2MBPS);
- pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(IR, INPUT);
- }
- void loop() {
- network.update();
- //===== Receiving =====//
- while ( network.available() ) { // Is there any incoming data?
- RF24NetworkHeader header;
- unsigned long buttonState;
- network.read(header, &buttonState, sizeof(buttonState)); // Read the incoming data
- digitalWrite(led, !buttonState); // Turn on or off the LED
- }
- //===== Sending =====//
- unsigned long irV = digitalRead(IR); // Read IR sensor
- RF24NetworkHeader header8(node01);
- bool ok = network.write(header8, &irV, sizeof(irV)); // Send the data
- }
在本段代码中,我们使用header.from_node属性来获取数据来自哪个节点的信息。 如果输入数据来自主设备,我们用它来控制伺服,如果输入数据来自节点012,我们用它来控制LED。 在节点012,我们有发送和接收。 红外传感器控制节点01处的前面提到的LED,这里的LED是来自主机上的按钮的控制。
节点022的代码 - /*
- Arduino Wireless Network - Multiple NRF24L01 Tutorial
- == Node 022 (child of Node 02)==
- */
- #include <RF24Network.h>
- #include <RF24.h>
- #include <SPI.h>
- #define led1 2
- #define led2 3
- #define led3 4
- #define led4 5
- RF24 radio(10, 9); // nRF24L01 (CE,CSN)
- RF24Network network(radio); // Include the radio in the network
- const uint16_t this_node = 022; // Address of our node in Octal format ( 04,031, etc)
- const uint16_t master00 = 00; // Address of the other node in Octal format
- void setup() {
- SPI.begin();
- radio.begin();
- network.begin(90, this_node); //(channel, node address)
- radio.setDataRate(RF24_2MBPS);
- pinMode(led1, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(led2, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(led3, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(led4, OUTPUT);
- }
- void loop() {
- network.update();
- //===== Receiving =====//
- while ( network.available() ) { // Is there any incoming data?
- RF24NetworkHeader header;
- unsigned long potValue;
- network.read(header, &potValue, sizeof(potValue)); // Read the incoming data
- // Turn on the LEDs as depending on the incoming value from the potentiometer
- if (potValue > 240) {
- digitalWrite(led1, HIGH);
- } else {
- digitalWrite(led1, LOW);
- }
- if (potValue > 480) {
- digitalWrite(led2, HIGH);
- } else {
- digitalWrite(led2, LOW);
- }
- if (potValue > 720) {
- digitalWrite(led3, HIGH);
- } else {
- digitalWrite(led3, LOW);
- }
- if (potValue > 960) {
- digitalWrite(led4, HIGH);
- } else {
- digitalWrite(led4, LOW);
- }
- }
- }
最后,使用来自主机上的另一个电位器的数据来控制节点022处的LED。
因此,总而言之,如果一切正常连接,并且所有节点始终处于活动状态,通过精确寻址节点就可以完成我们的工作,所有繁重的工作都由强大的RF24Network库执行。
以上就是本篇文章的全部内容,希望您能喜欢这篇Arduino文章,并能学到一些新东西。 如果遇到任何问题,请随时在下面进行回复。 |
 |手机版|YiBoard一板网
( 冀ICP备18020117号 )
|手机版|YiBoard一板网
( 冀ICP备18020117号 )