|
在本篇文章中,我们将主要介绍如何使用Arduino和LM35温度传感器设计基于温度的风扇速度控制和监控。微控制器根据要求控制电风扇的速度,并允许动态和更快的控制,并且LCD使系统易于使用。 LCD面板上同时显示以摄氏度为单位的感测温度和以百分比表示的风扇速度。
该项目的主要应用领域是空调、热水器、融雪机、烤箱、热交换、熔炉、保温箱和热水浴等场合。
所需的组件 ● Arduino UNO开发板 ● LM35温度传感器 ● 2N2222晶体管 ● 1602 LCD显示屏 ● 12V DC风扇 ● 1N4007二极管 ● LED指示灯 ● 12伏电池/适配器
电路图和连接
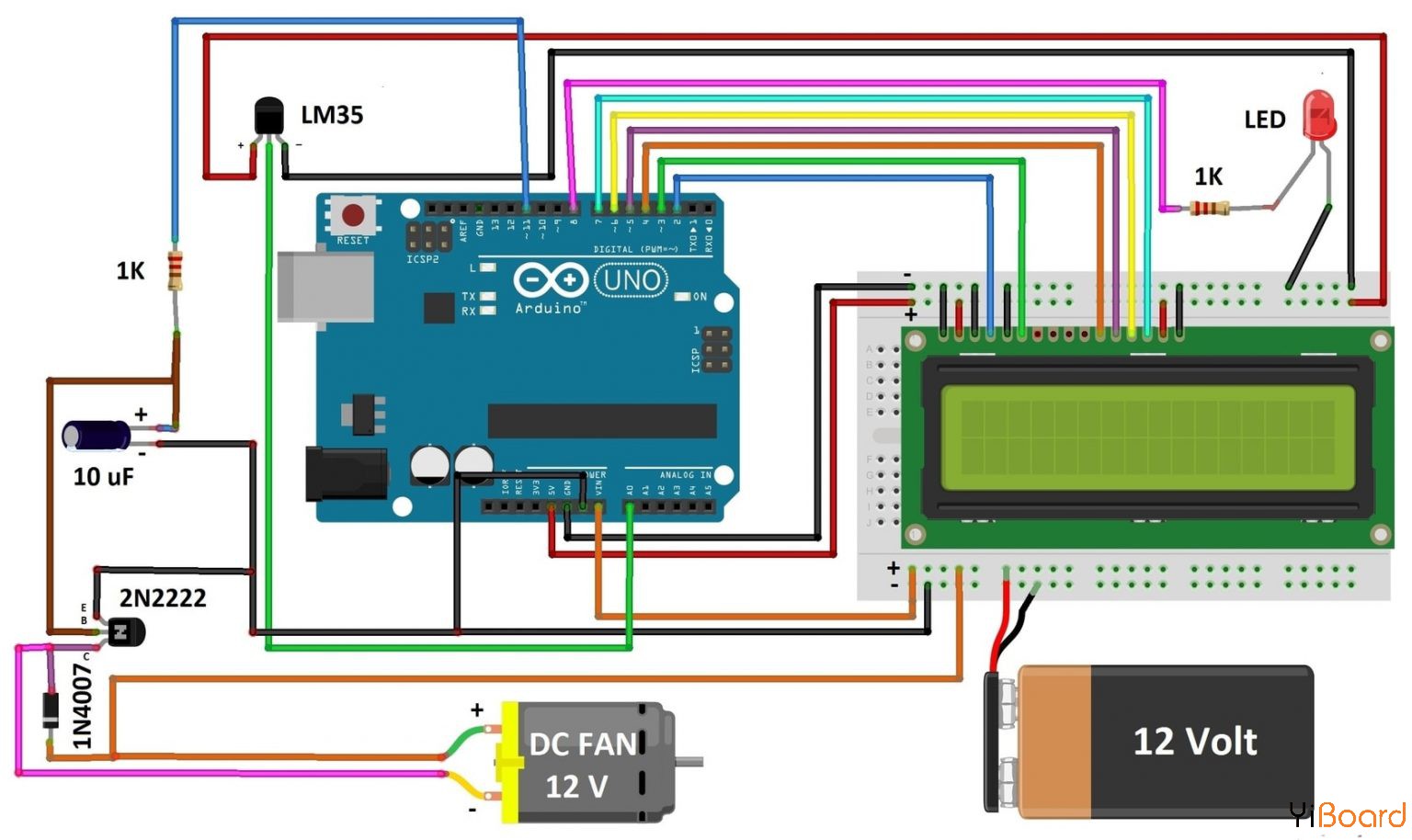
上面显示了使用Arduino和LM35进行基于温度的风扇速度控制和监控的电路图。 Arduino是电路的主控部分,因为它控制所有功能。 LM35是一种精密集成电路,其输出电压与摄氏温度成线性比例。额定温度范围为-55°C至150°C。它具有+ 10.0mV /摄氏度的线性比例因子。 2N2222晶体管用作开关并根据温度控制风扇速度。 1N4007二极管控制风扇不受损坏。温度超过60°C时,LED灯点亮。
电路工作过程 温度传感器LM35感测温度并将其转换为电(模拟)信号,该信号被应用于Arduino UNO开发板的ATmega328微控制器。模拟值转换为数字值。这样,风扇的温度和速度的感测值显示在LCD上。当温度超过30°C时,风扇开始旋转。
使用了低频脉宽调制(PWM)信号,其占空比可以改变以调节风扇的速度。此处可以使用价格便宜的单通道小通过晶体管,如2N222或BD139。这种方法很有效,因为传输晶体管被用作开关。
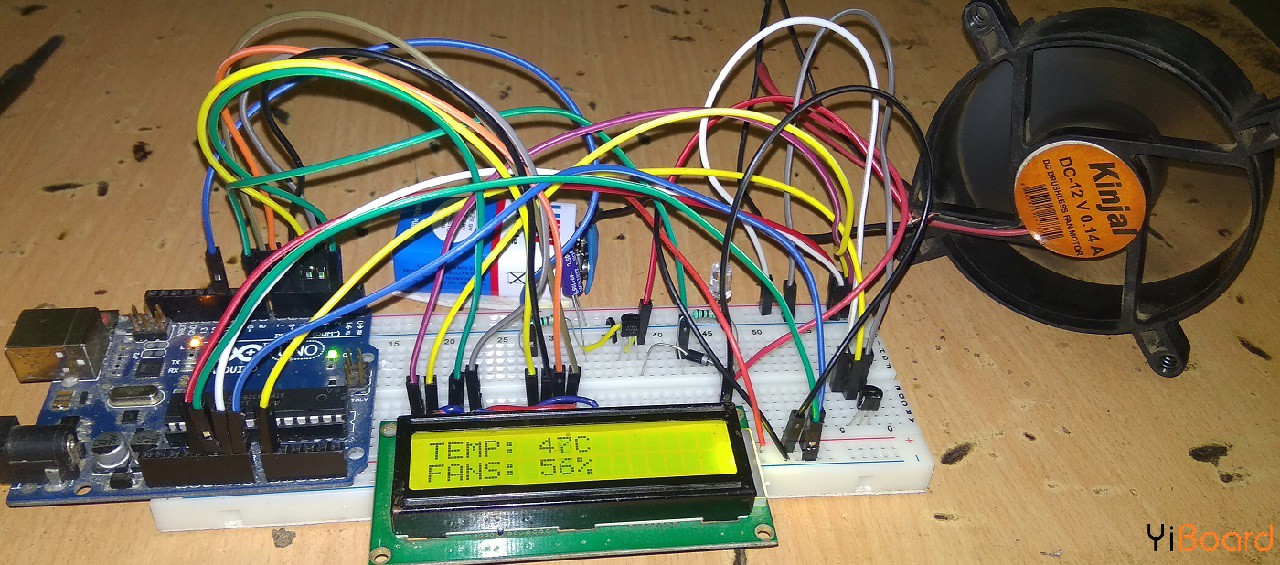
源代码/程序 下面给出了使用Arduino和LM35进行基于温度的风扇速度控制和监控的程序。只需复制此代码并将其粘贴到您的Arduino IDE中,编译代码,然后上传。
- #include <LiquidCrystal.h>
- LiquidCrystal lcd(2,3,4,5,6,7);
- int tempPin = A0; // the output pin of LM35
- int fan = 11; // the pin where fan is
- int led = 8; // led pin
- int temp;
- int tempMin = 30; // the temperature to start the fan 0%
- int tempMax = 60; // the maximum temperature when fan is at 100%
- int fanSpeed;
- int fanLCD;
- void setup() {
- pinMode(fan, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
- pinMode(tempPin, INPUT);
- lcd.begin(16,2);
- Serial.begin(9600);
- }
- void loop()
- {
- temp = readTemp(); // get the temperature
- Serial.print( temp );
- if(temp < tempMin) // if temp is lower than minimum temp
- {
- fanSpeed = 0; // fan is not spinning
- analogWrite(fan, fanSpeed);
- fanLCD=0;
- digitalWrite(fan, LOW);
- }
- if((temp >= tempMin) && (temp <= tempMax)) // if temperature is higher than minimum temp
- {
- fanSpeed = temp;//map(temp, tempMin, tempMax, 0, 100); // the actual speed of fan//map(temp, tempMin, tempMax, 32, 255);
- fanSpeed=1.5*fanSpeed;
- fanLCD = map(temp, tempMin, tempMax, 0, 100); // speed of fan to display on LCD100
- analogWrite(fan, fanSpeed); // spin the fan at the fanSpeed speed
- }
- if(temp > tempMax) // if temp is higher than tempMax
- {
- digitalWrite(led, HIGH); // turn on led
- }
- else // else turn of led
- {
- digitalWrite(led, LOW);
- }
- lcd.print("TEMP: ");
- lcd.print(temp); // display the temperature
- lcd.print("C ");
- lcd.setCursor(0,1); // move cursor to next line
- lcd.print("FANS: ");
- lcd.print(fanLCD); // display the fan speed
- lcd.print("%");
- delay(200);
- lcd.clear();
- }
- int readTemp() { // get the temperature and convert it to celsius
- temp = analogRead(tempPin);
- return temp * 0.48828125;
- }
|